MAT-HS.G-CO.06
|
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions
MAT-HS.G-CO.06 Use geometric descriptions of rigid motions to transform figures and to predict the effect of a given rigid motion on a given figure; given two figures, use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to decide if they are congruent.
|
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
- I can define congruent.
- I can define similarity.
- I can match corresponding sides in two or more figures.
- I can match corresponding angles in two or more figures.
- I can identify types of transformations such as translation, rotation, and reflection.
- I know that a translation is a slide.
- I know that a rotation is a turn.
- I know that a reflection is flip.
- I can illustrate transformations on a coordinate plane.
- I can plot points/ordered pairs on a coordinate plane.
- I can use the fact that rigid transformations preserve size and shape to connect the idea and definition of congruence.
Reasoning Targets
- I can compare figures to determine if they are congruent.
- I can compare figures to determine if they are similar.
- I can use a proportion to solve the unknown side or angle of a shape.
- I can use a ratio to compare the side lengths or angles of a shape.
- I can predict the coordinates of a transformed figure.
- I can find the scale factor of two similar figures when given the dimensions.
- I can use descriptions of rigid motion and transformed geometric figures to predict the effects rigid motion has on figures in the coordinate plane.
Skills (Performance) Targets
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
| 4.0 |
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
| 3.0 |
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 2.0 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| 1.0 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.07
|
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions
MAT-HS.G-CO.07 Use the definition of congruence in terms of rigid motions to show that two triangles are congruent if and only if corresponding pairs of sides and corresponding pairs of angles are congruent.
|
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
- I can determine congruence and similarity among geometric objects.
- I can use similarity or congruence to solve for a missing side/angle.
Skills (Performance) Targets
- I can use the definition of congruence, based on rigid motion, to show two triangles are congruent if and only if their corresponding sides and corresponding angles are congruent.
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
|
Advanced
|
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
|
Proficient
|
The student can:
· show two figures are congruent after a sequence of rigid motions (translations, reflections, rotations).
· use the definition of congruence as a test to see if two figures are congruent (if and only if they have the same shape and size).
|
-A student finds two triangles on two different pieces of patty paper. He places them on the desk to compare them. He slides and then turns the paper so that the two triangles on are on top of each other and then he notices that he needs to flip one of the papers so that they will land exactly on top of each other. The student concludes that they are copies of each other. Mathematically, what did this procedure prove about the triangles? |
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
|
Progressing
|
There are no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes as the student can:
· recognize and recall terminology to answer questions.
· use composite transformations to map one figure onto another.
· recognize the effects of rigid motion on orientation and location of a figure.
|
1. A rigid motion is the same as:
A) A mapping
B) A transformation
C) An Isometric transformation
D) A proportional expansion
2. Congruence can be found through isometric transformations because they preserve key characteristics of the shape. Which of the following is NOT one of the characteristics that an isometry preserves?
A)Angle size
B) Location on the plane
C)Distance between points
D) Collinearity of points
3. K(x,y) - - - - - > (-x,-y)could represent a transformation that could establish congruence. T or F
|
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
|
Beginning
|
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.08
|
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Understand congruence in terms of rigid motions
MAT-HS.G-CO.08 Prove two triangles are congruent using the congruence theorems such as ASA, SAS, and SSS.
|
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
- I can determine congruence and similarity among geometric objects.
- I can use similarity or congruence to solve for a missing side/angle.
Skills (Performance) Targets
- I can use the definition of congruence, based on rigid motion, to explain the triangle congruence criteria; ASA, SSS, and SAS.
Product Targets
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
|
Advanced
|
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations.
- The student will be able to explain why triangles in a three dimensional figure are congruent.
- The student will be able to prove statements by first proving congruent triangles.
- The student will be able to explain why AA or SSA gives you congruent triangles only sometimes.
|
-

|
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
|
Proficient
|
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations.
The student can perform all the actions for each concept listed below:
|

Jennifer states that ∆ABC ≅ ∆DEF can be proven by either ASA or AAS. Joshua disagrees – he says it can only be done by ASA because in ∆ABC it is missing the matching symbol to ∠D so we do not know if ∠A ≅ ∠D. Who is correct? Explain.
|
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
|
Progressing
|
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content).
- The student can recognize and recall terminology to answer questions.
|
 
|
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| Beginning |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.09
|
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Prove geometric theorems
MAT-HS.G-CO.09 Prove and apply theorems about lines and angles.
Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. |
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
Skills (Performance) Targets
- I can prove theorems pertaining to lines and angles.
- I can prove vertical angles are congruent.
- I can prove when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent.
- I can prove points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints.
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
| 4.0 |
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
| 3.0 |
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 2.0 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| 1.0 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.09.a |
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Prove geometric theorems
MAT-HS.G-CO.09.a Prove theorems about lines and angles.
Theorems include but are not limited to: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints.
|
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
Skills (Performance) Targets
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
| Advanced |
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations.
Concepts:
Vertical Angles
Angles created by parallel lines and a transversal
Perpendicular Bisector theorems
|
- |
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
| Proficient |
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations.
- Identify relevant given information
- Arrange reasoning in a logical sequence
- Support reasoning using appropriate justifications (theorems, postulates, definitions, etc.)
Concepts:
Vertical Angles
Angles created by parallel lines and a transversal
Perpendicular Bisector theorems
|

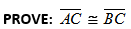
|
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| Progressing |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content).
- partially prove but reasoning has gaps, steps missing, incorrect reasoning, etc.
- recall theorems, definitions, and postulates
- fill out justification given a statement
Concepts:
Vertical Angles
Angles created by parallel lines and a transversal
Perpendicular Bisector theorems
|
 |
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| Beginning |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.09.b |
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Prove geometric theorems
MAT-HS.G-CO.09.b Apply theorems about lines and angles.
Theorems include: vertical angles are congruent; when a transversal crosses parallel lines, alternate interior angles are congruent and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. (Focus is on applying the theorems for C-CO.9B) |
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
Skills (Performance) Targets
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
| Advanced |
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations.
Concepts:
Vertical Angles
Angles created by parallel lines and a transversal
Perpendicular Bisector theorems
|

Solve for x and y.
|
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
| Proficient |
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations.
- Identify the relevant information
- Apply geometric relationships to create an algebraic model for the situation
- Solve and answer the given question (Ex. Solve for the given variable, Find the angle measurement)
Concepts:
Vertical Angles
Angles created by parallel lines and a transversal
Perpendicular Bisector theorem
|

Solve for x.

Solve for x and y.
|
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| Progressing |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content).
- can recognize and recall angle pairs
- can apply postulates, definitions, properties, and theorems to identify angle measurements
Concepts:
Vertical Angles
Angles created by parallel lines and a transversal
Perpendicular Bisector theorems
|

Example 2
 
|
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| Beginning |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.10
|
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Prove geometric theorems
MAT-HS.G-CO.10 Prove and apply theorems about triangles.
Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180°; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point. |
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
Skills (Performance) Targets
- I can prove theorems about triangles.
- I can prove the measures of interior angles of a triangle have a sum of 180°.
- I can prove base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent.
- I can prove the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length.
- I can prove the medians of a triangle meet at a point.
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
| 4.0 |
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
| 3.0 |
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 2.0 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| 1.0 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.10.a |
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Prove geometric theorems
MAT-HS.G-CO.10.a Prove theorems about triangles.
(Theorems include but are not limited to: Measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180 degrees; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point.)
(Focus on proving for this proficiency scale)
|
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
Skills (Performance) Targets
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
| Advanced |
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations.
- Analyze a proof with errors and make corrections
|
- |
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
| Proficient |
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations.
-
Identify relevant given information
-
Arrange reasoning in a logical sequence
-
Support reasoning using appropriate justifications (theorems, postulates, definitions, etc.)
|
Midsegment of a Triangle Proof
Triangle Interior Angle Proof
Prove a Triangle is Isosceles
|
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| Progressing |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content).
- partially prove but reasoning has gaps, steps missing, incorrect reasoning, etc.
- recall theorems, definitions, and postulates
- fill out justification given a statement
|
Given a statement, the student can fill out the justification. (skeleton proof) |
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| Beginning |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.10.b |
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Prove geometric theorems
MAT-HS.G-CO.10.b Apply theorems about triangles.
(Theorems include: measures of interior angles of a triangle sum to 180 degrees; base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent; the segment joining midpoints of two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and half the length; the medians of a triangle meet at a point.
(Focus on Applying)
|
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
Skills (Performance) Targets
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
| Advanced |
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations.
- Analyze a solution and correct the errors
- Investigate and provide multiple methods for finding a solution to a given problem
|

Find the measures of these angles in two different ways. Explain the steps you took for each method.
|
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
| Proficient |
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations.
- Apply theorems (postulates, definitions, etc.) about triangles to solve problems
- Justify how to set up a problem using theorems (postulates, definitions, etc.) about triangles
|

  
|
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| Progressing |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content).
- Identify or relate the theorem used to set up the problem
- Define the vocabulary associated with triangle theorems
- Can identify the components of triangles
|
- |
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| Beginning |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|
MAT-HS.G-CO.11
|
MAT-HS Targeted Standards
(G) Concept: Geometry
(CO) Domain: Congruence
Cluster: Prove geometric theorems
MAT-HS.G-CO.11 Prove and apply theorems about parallelograms.
Theorems include: opposite sides are congruent, opposite angles are congruent, the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other, and conversely, rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals. |
Student Learning Targets:
Knowledge Targets
Reasoning Targets
Skills (Performance) Targets
- I can prove theorems about parallelograms.
- I can prove opposite sides are congruent.
- I can prove opposite angles are congruent.
- I can prove the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
- I can prove rectangles are parallelograms with congruent diagonals.
Product Targets
|
Proficiency Scale
| Score |
|
Description |
Sample Activity
|
| 4.0 |
In addition to Score 3.0, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding more complex material that go beyond end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
3.5 |
In addition to Score 3.0 performance, the student demonstrates in-depth inferences and applications regarding the more complex content with partial success. |
| 3.0 |
“The Standard.” The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding any of the information and processes that were end of instruction expectations. |
- |
| |
2.5 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 2.0 |
The student demonstrates no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
1.5 |
The student demonstrates partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures (Score 3.0 content). |
| 1.0 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) and some of the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
- |
| |
0.5 |
With help, the student demonstrates a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes (Score 2.0 content) but not the more complex ideas and processes (Score 3.0 content). |
| 0.0 |
Even with help, the student demonstrates no understanding or skill. |
- |
Resources
|
|

